Introduction
- Java 8 provides Streams API , that converts collection type to stream type. Once we have Stream, we can perform N number of operations on it that is defined in Streams API.
- In this blog we will focus on skip() and limit() methods.
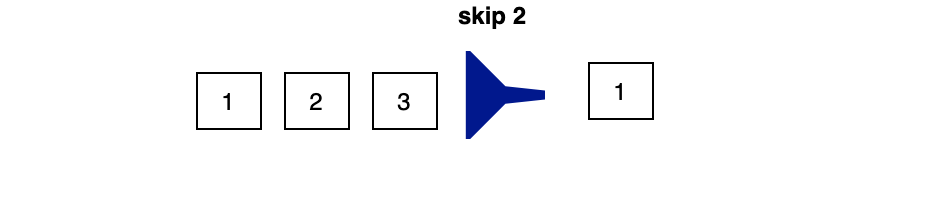
Skip()
- Skip operation is useful when we want to discard some number elements from actual collection.
- If we 100 elements and we want to skip first 10 elements then we can just pass 10 as number to skip(10).
Stream<T> skip(long n)
- Returns a stream consisting of the remaining elements of this stream after discarding the first n elements of the stream.
- If this stream contains fewer than n elements then an empty stream will be returned.
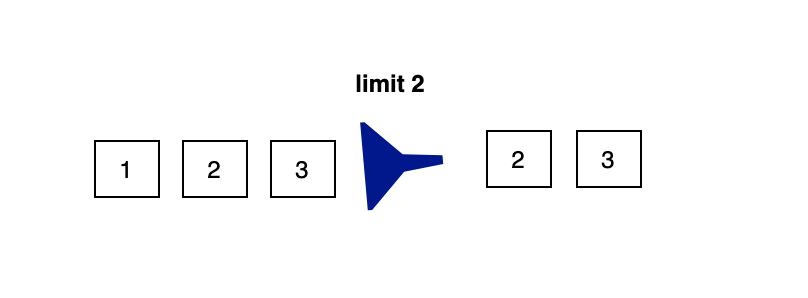
Limit()
- Limit would be truncated to the provided maxSize, means we will get maxSize number of elements from totalElements.
Stream<T> limit(long maxSize)
Returns a stream consisting of the elements of this stream, truncated to be no longer than maxSize in length.
Use Case
- Let’s say we have file with below contents. Generally files consist of some header and footer that provides metadata of the file. I have seen this kind of structure in financial domain where we transfer file along with some metadata as header and footer.
- Header generally specify schema and data time, while Footer specifies total number of records.

- Our goal is to filter the header , footer and file content .
Use of Skip() & Limit()
- Step1: Read file as List of string using Java.nio utility and print the content.
List<String> fullFileContent = Files.readAllLines(Path.of("/Users/suraj.mishra/Desktop/demo.txt"));
fullFileContent.stream().forEach(a-> System.out.println(a));
System.out.println("-------------------");

- Now lets convert List of string to stream using stream() method skip header by passing skip(1).
List<String> contentWithFooter = fullFileContent
.stream()
.skip(1)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
- Now we have content with footer, we have skipped header .
- Next we will use limit() to only filter content and not the footer. Here contentWithFooter.size() only get fileContent and doesn’t allow the footer which is last entry.
List<String> justContent = contentWithFooter
.stream()
.limit(contentWithFooter.size() - 1)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
justContent.stream().forEach(a-> System.out.println(a));
System.out.println("-------------------");
- We can verify our result easily by printing the filtered content.

- We can use entire skip and limit operations in single chained operation as below.
- Reason we are using fullFileContent.size()-2 here is because this list contains header as well, hence subtracting (total — (header+footer ))
List<String> filContents = fullFileContent
.stream()
.skip(1)
.limit(fullFileContent.size() - 2)
.collect(Collectors.toList());
filContents.stream().forEach(a-> System.out.println(a));
Conclusion
- In this blog we discuss practical application of Stream API’s Skip() and Limit() operation .
- They can be used together to operate on our collection more effectively .
Bonus Tip
- If you want to upskill your Java, you should definitely check out this bestseller course
